Using Boolean Logic as a Tool for Information Retrieval
Last Updated : 19 August 2025 15:08- ASO School of Engineering
- Binus Business School
- Doctor
- International Undergraduate
- Master
- Online Collaboration S1
- Online Master
- Online Undergraduate
- Regular Collaboration S1
- Regular Profession
- Undergraduate
- Undergraduate (Bandung)
- Undergraduate (Malang)
- Undergraduate (Medan)
- Undergraduate (Semarang)
In academic and research settings, information retrieval (IR) is a crucial process for finding relevant resources efficiently. One powerful technique used to enhance search precision is Boolean Logic.
Boolean Logic allows users to combine keywords with logical operators to either narrow or broaden search results. This technique is especially useful when working with academic databases such as Scopus, PubMed, or other scholarly search engines.
The main Boolean operators are AND, OR, and NOT, each serving a specific purpose to control search results.
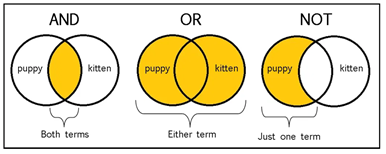
1. AND Operator
-
Function: Displays results that contain all keywords connected by the AND operator.
-
Example:
climate change AND renewable energy
This query will only return documents that include both phrases. -
Benefit: Narrows down the results, making the search more specific and relevant.
2. OR Operator
-
Function: Retrieves results that include any of the keywords connected by the OR operator.
-
Example:
teenagers OR adolescents
Results will include documents containing either term or both. -
Benefit: Broadens the search scope by including synonyms or related terms, useful when different terms may describe the same concept.
3. NOT Operator
-
Function: Excludes documents containing a specific keyword, ensuring results do not include that term.
-
Example:
machine learning NOT deep learning
The results will include documents about “machine learning” but exclude those that mention “deep learning.” -
Benefit: Helps eliminate irrelevant topics or filter out overly broad information.
4. Combining Operators for Complex Searches
-
Using Multiple Operators:
Users can combine several Boolean operators to create more complex search queries, for example:(COVID-19 OR coronavirus) AND (vaccine OR immunization) AND NOT children -
Prioritization:
Parentheses()should be used to set priority and ensure the database processes certain parts of the query first.
5. Benefits of Using Boolean Logic in Information Retrieval
-
Better Control: Allows users to narrow or expand search results as needed.
-
Improved Relevance: Reduces irrelevant results, making searches more accurate.
-
Time Efficiency: Saves time by delivering more targeted results quickly.
By applying Boolean Logic, the process of retrieving information from databases or search engines becomes more effective and efficient, enabling researchers to find relevant literature without going through thousands of unrelated results.











